4 Childhood Obesity Reasons and Problems!
Introduction
Childhood obesity is a growing concern in modern society, affecting children across the globe. In this comprehensive article, we delve deep into the various factors contributing to weight problems in children, exploring the implications on their physical and emotional well-being. Our aim is to provide you with valuable insights and guidance to address childhood obesity and help you make informed decisions for your child’s health.
The Prevalence of Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity has reached alarming levels in recent years. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of overweight or obese children under the age of five exceeds 41 million worldwide. This condition not only leads to immediate health issues but also puts children at risk of developing chronic diseases later in life.
Causes of Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity is a multifactorial problem, arising from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some common causes include:
1. Unhealthy Eating Habits

Unhealthy eating habits significantly contribute to childhood obesity. The consumption of calorie-dense, processed foods high in sugars, fats, and salt leads to excessive calorie intake and a lack of essential nutrients. Children often indulge in sugary snacks, fast food, and sugary beverages, which can result in weight gain and other health issues. Poor eating habits, such as skipping meals or frequent consumption of high-calorie snacks, disrupt the balance of energy intake and expenditure, leading to an unhealthy weight. It is essential to promote a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting the intake of unhealthy foods to combat child obesity and foster a healthier lifestyle.
2. Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is a major contributing factor to childhood obesity. With the prevalence of screen-based entertainment and digital devices, children are spending more time sitting and engaging in passive activities, leading to reduced physical activity levels. Insufficient exercise not only hinders calorie expenditure but also negatively impacts overall health and well-being. Regular physical activity is essential for children to maintain a healthy weight, strengthen muscles and bones, and promote cardiovascular health. Encouraging active play, outdoor activities, and limiting screen time can help combat the effects of a sedentary lifestyle and play a crucial role in preventing and managing child obesity.

3. Genetic Predisposition

Genetics significantly influences a child’s susceptibility to obesity, as certain genetic variants can affect their metabolism, fat storage, and appetite regulation. While environmental factors play a role in weight management, understanding the genetic predisposition can provide crucial insights into the risk of developing obesity. By recognizing these genetic factors, parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals can tailor interventions and lifestyle modifications to support children in maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of obesity-related health issues in the long run.
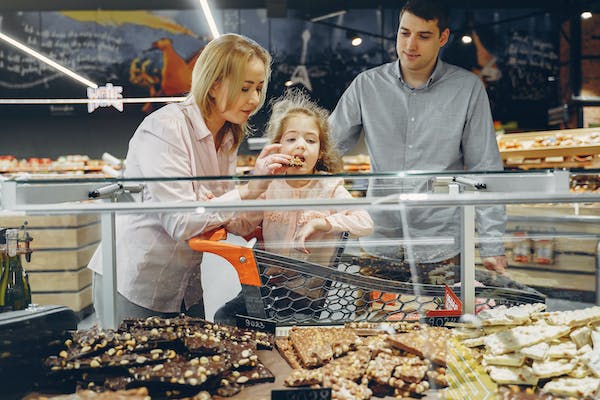
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in child obesity, influencing a child’s access to healthy food options and opportunities for physical activity. Factors such as the availability and affordability of nutritious foods, the presence of fast-food outlets in the neighborhood, and the lack of safe outdoor spaces for play can contribute to unhealthy dietary choices and reduced physical activity. Additionally, socio-economic conditions can impact a family’s ability to afford healthy foods and participate in extracurricular activities that promote an active lifestyle. Addressing these environmental influences is crucial in creating a supportive and healthy environment for children, fostering better eating habits, and encouraging regular physical activity to combat the rising rates of childhood obesity.

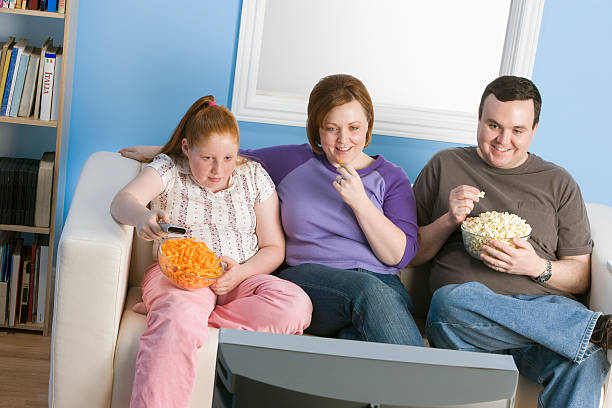
Health Risks Associated with Childhood Obesity
Childhood obesity exposes children to a wide range of health risks, both physical and psychological. Some of the significant health issues include:
1. Type 2 Diabetes
Childhood obesity is closely linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, a serious metabolic disorder. Excess weight and body fat can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond effectively to insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, this condition can progress to type 2 diabetes, especially in children who are overweight or obese. The early onset of diabetes in childhood can have severe health implications, including cardiovascular complications and a higher risk of developing other chronic conditions later in life. Addressing child obesity through healthy lifestyle interventions, such as balanced nutrition and regular physical activity, is crucial in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and promoting better overall health outcomes for children.
2. Cardiovascular Problems
Child obesity is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular problems in children. Excess body weight puts a strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to conditions like high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and atherosclerosis, even at a young age. These factors increase the likelihood of developing heart disease and other cardiovascular complications later in life. Moreover, obese children may experience reduced physical fitness, which further exacerbates their cardiovascular health. Addressing child obesity through lifestyle changes, including a balanced diet and regular physical activity, is essential in mitigating the risk of cardiovascular problems and promoting better heart health for children. Early intervention and prevention efforts can contribute to a healthier future for our young population.
3. Respiratory Disorders
Child obesity is closely linked to an increased prevalence of respiratory disorders in children. Excess body weight can place additional pressure on the respiratory system, leading to breathing difficulties such as asthma and sleep apnea. Obese children often experience reduced lung function, which can worsen respiratory symptoms and hinder their overall well-being. Additionally, the accumulation of fat in the chest and abdomen can further restrict lung expansion, making it harder for children to breathe properly. Addressing child obesity through healthy lifestyle modifications, such as regular physical activity and a balanced diet, is crucial in reducing the risk of respiratory disorders and improving the respiratory health of children. By taking proactive steps to combat child obesity, we can promote better lung function, overall respiratory health of our children.
4. Psychological Impact
Childhood obesity can have a profound psychological impact on children. The stigma and social pressures associated with being overweight can lead to low self-esteem and poor body image, affecting a child’s emotional well-being. Obese children may experience increased feelings of sadness, anxiety, and depression, as they face challenges in social interactions and peer relationships. Moreover, the negative perceptions and comments from others may further exacerbate their emotional struggles. Addressing child obesity not only improves physical health but also plays a crucial role in promoting positive mental health outcomes. By providing support, understanding, and encouraging healthy lifestyle habits, we can help children build confidence and resilience, fostering a positive outlook and better psychological well-being.
Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity
Preventing and managing childhood obesity requires a comprehensive approach involving parents, caregivers, schools, and the community. Here are some effective strategies:
1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in the prevention and management of childhood obesity. Providing children with a diverse and nutrient-rich diet ensures they receive essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients necessary for their growth and development without excessive calorie intake. A balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats helps regulate hunger and satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating. It also promotes optimal metabolism and energy expenditure, supporting a healthy weight. Moreover, a well-balanced diet strengthens the immune system, improves overall health, and reduces the risk of obesity-related health issues. By instilling healthy eating habits in children from an early age and encouraging a varied and balanced diet, we can effectively prevent and manage child obesity, setting the foundation for a lifetime of good health and well-being.


2. Regular Physical Activity

Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in the prevention and management of child obesity. Engaging in regular exercise helps children burn calories, maintain a healthy weight, and improve their overall fitness levels. Physical activity also supports the development of strong muscles and bones, enhancing a child’s physical well-being. Additionally, regular exercise aids in reducing the risk of various health conditions associated with obesity, such as cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, physical activity promotes positive mental health by releasing endorphins, which can help reduce stress and improve mood. Encouraging children to participate in age-appropriate and enjoyable physical activities fosters a lifelong habit of staying active, leading to a healthier and happier lifestyle. By prioritizing regular physical activity, we can effectively prevent and manage child obesity, paving the way for a healthier future for our children.
3. Family Involvement
The involvement of the family in adopting healthy habits is paramount in the prevention and management of child obesity. When parents and caregivers lead by example and embrace healthy lifestyle choices, children are more likely to follow suit. Family involvement creates a supportive environment that promotes nutritious eating habits and regular physical activity. Eating meals together as a family can encourage the consumption of balanced and wholesome foods, while engaging in fun, active activities together fosters a love for exercise. By collectively prioritizing health and wellness, families can instill positive habits in children from an early age, reducing the risk of child obesity and laying the foundation for a lifetime of well-being.
4. Education and Awareness
Education and awareness play a vital role in the prevention and management of childhood obesity. By providing parents, caregivers, and children with valuable information about healthy eating habits, the importance of regular physical activity, and the risks associated with obesity, we empower them to make informed choices. Raising awareness about the long-term health implications of child obesity helps create a sense of urgency in taking proactive measures. Educating the community about practical strategies for maintaining a healthy lifestyle fosters a supportive environment for children, making it easier to adopt and sustain healthy habits. By promoting education and awareness, we can effectively combat child obesity and work towards building a healthier future for the younger generations.
Conclusion
Childhood obesity is a pressing issue that demands immediate attention and action. By understanding the causes, health risks, and preventive measures, we can work together to combat this growing problem. Emphasizing a healthy lifestyle, balanced diet, and regular physical activity will not only address childhood obesity but also ensure a brighter, healthier future for our children. Let us unite in this endeavor to create a healthier generation and a better world for our kids.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
10 FAQs about Child Obesity
What is childhood obesity?
Childhood obesity refers to a condition in which a child has an excess amount of body fat, resulting in a higher-than-healthy weight for their age, height, and gender. It is determined by calculating the body mass index (BMI) of a child, and obesity is diagnosed when the BMI is above the 95th percentile for children of the same age and sex.
What are the common causes of child obesity?
Child obesity is usually caused by a combination of factors, including unhealthy eating habits, sedentary lifestyle, genetic predisposition, and environmental influences. Consuming calorie-dense, processed foods, and spending excessive time in front of screens contribute to weight gain.
Why is child obesity a concern?
Child obesity is a serious health concern as it increases the risk of various health problems, such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, respiratory disorders, and psychological issues. It can also lead to long-term health consequences in adulthood if not addressed early.
How can child obesity be prevented?
Preventing child obesity involves promoting a healthy lifestyle. Encouraging a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, along with regular physical activity, is key to preventing obesity. Limiting screen time and providing opportunities for active play are also essential.
What are the health risks associated with child obesity?
Child obesity increases the risk of various health problems, including type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, asthma, sleep apnea, joint problems, and emotional issues like low self-esteem and depression.
How can parents support their child in managing obesity?
Parents can support their child in managing obesity by being positive role models. Providing nutritious meals, encouraging physical activity, and involving the whole family in healthy lifestyle choices can make a significant difference. Consulting with healthcare professionals for guidance and support is also recommended.
Can genetics play a role in child obesity?
Yes, genetics can influence a child’s susceptibility to obesity. Children with obese parents are more likely to inherit certain genes that affect metabolism and fat storage, making them more prone to gaining weight.
How can schools contribute to addressing child obesity?
Schools can play a vital role in addressing child obesity by promoting physical education, providing nutritious meals in the cafeteria, and creating a supportive environment for active play during recess and after-school activities.
Is it possible to reverse child obesity?
Yes, child obesity can be reversed through lifestyle changes. Adopting a healthier diet and increasing physical activity can lead to weight loss and improved overall health. It is crucial to take a gradual and sustainable approach to achieve lasting results.
When should I seek medical help for my child's obesity?
If you are concerned about your child’s weight and suspect they may be obese, it is essential to consult with a pediatrician or a healthcare professional. They can assess your child’s BMI, provide personalized recommendations, and offer guidance on managing obesity effectively.
One Response