Introduction
Many individuals strive to lead a healthy lifestyle. Maintaining an optimal body weight is an essential aspect of overall well-being. One of the widely used methods to assess weight in relation to height is the Body Mass Index (BMI). In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of BMI, its significance in gauging a healthy weight, its limitations, and how you can use it to improve your overall health.
What is Body Mass Index?
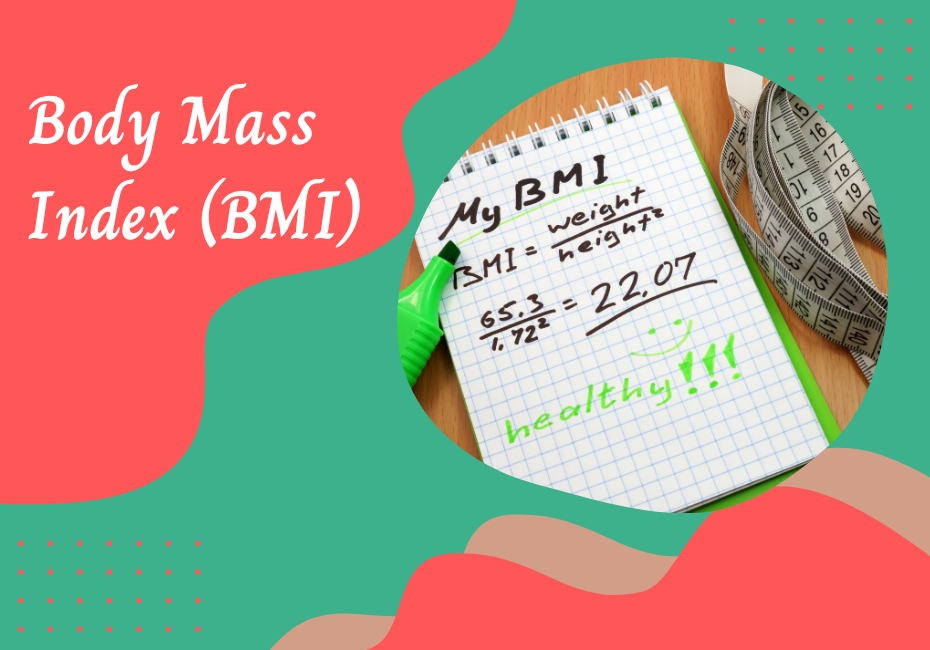
BMI is a numeric value calculated based on a person’s weight and height. It provides an estimate of body fat and is widely used by healthcare professionals as an initial screening tool to categorize weight status. The formula to calculate BMI is: BMI = (Weight in kilograms) / (Height in meters)2
Let’s learn what is Body Mass Index with an example. There are two persons say, John and Carl. They’re both around the same height, weight, and consequently, they have the same Body Mass Index or BMI say 28.5. But if you split them open or just compare the results of their body scans you can see a slight difference. John has more body fat than Carl, and Carl has more muscle than John. Though, BMI is a knownmethod to assess that, how much a person is at risk of diseases related to obesity with respect to his weight, its results can be quite misleading and less modulated than we would like.
The Significance of Body Mass Index
Maintaining a healthy BMI is crucial as it has been associated with various health benefits. Here’s why BMI is considered significant:
1. BMI and Health Risk Assessment
Body Mass Index helps in assessing the risk of developing weight-related health conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and hypertension. People with a BMI in the normal range generally have lower health risks compared to those with either low or high BMI.
2. Body Mass Index and Weight Management
BMI serves as a useful tool for individuals aiming to manage their weight. Whether you want to lose, gain, or maintain weight, understanding your Body Mass Index can guide your efforts and help you set realistic goals.
3. BMI and Overall Well-being
Maintaining a healthy BMI positively impacts overall well-being. Achieving and sustaining a balanced BMI contributes to increased energy levels, improved sleep quality, and enhanced self-esteem.
Understanding the BMI Categories
BMI is typically divided into several categories to help assess weight status. These categories serve as a general guideline, but it’s essential to remember that individual factors like muscle mass, age, and sex can influence the interpretation.
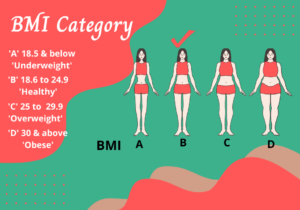
1. Underweight (BMI < 18.5)
Individuals with a BMI below 18.5 are considered underweight. Being underweight may indicate potential nutrient deficiencies and health risks. If you fall into this category, seeking professional advice to improve your nutritional intake and overall health is crucial.
2. Normal Weight (BMI 18.5 - 24.9)
A person having BMI in the range of 18.5 to 24.9 is considered to have normal weight. Individuals in this category generally have a lower risk of weight-related health issues and are encouraged to maintain their weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
3. Overweight (BMI 25.0 - 29.9)
Being overweight, with a BMI between 25.0 to 29.9, may increase the risk of health problems such as diabetes and heart disease. Adopting healthier eating habits and engaging in regular exercise can be beneficial for individuals in this category.
4. Obese (BMI ≥ 30.0)
An individual with a BMI of 30.0 or higher is classified as obese. Obesity is associated with a higher risk of chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. Weight loss through a combination of diet, exercise, and professional support is often recommended for obese individuals to improve their health.
The Limitations of Body Mass Index
While Body Mass Index is a valuable screening tool, it does have its limitations, and it’s important not to rely solely on this measurement to assess overall health.

1. Not Accounting for Body Composition
BMI does not differentiate between fat, muscle, and bone mass. As a result, individuals with a high muscle mass may have a higher BMI, even though they have low body fat and are in good health.
2. Age and Sex Differences
Body Mass Index categories apply differently to different age groups and sexes. For instance, older adults may have a higher percentage of body fat that is considered healthy, while BMI thresholds for children and adolescents are age-specific.
3. Ethnic Variations
BMI classifications may not be equally applicable to all ethnic groups due to differences in body composition and fat distribution.
Calculating BMI - Step by Step
Calculating your Body Mass Index is a straightforward process that requires knowing your weight in kilograms and your height in meters. Follow the following steps for calculating BMI:
Step 1: Measure your weight on a reliable scale and record it in kilograms.
Step 2: Measure your height without shoes, standing straight against a wall, and record it in meters.
Step 3: Square your height (in meters).
Step 4: Divide your weight in kilograms by the squared height to obtain your BMI.
Once you have calculated your BMI, you can compare it with the standard categories to assess your weight status.
BMI's Role in Disease Prevention
Maintaining a healthy BMI can significantly reduce the risk of developing various chronic conditions. Let’s explore how BMI influences the prevention of certain diseases:
Achieving a healthy Body Mass Index is linked to improved cardiovascular health. Lower BMI levels are associated with reduced risks of heart disease and hypertension, as excess weight can strain the heart and blood vessels.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. By managing BMI through diet and exercise, individuals can reduce the likelihood of developing this condition.
3. Joint Health
Excessive body weight can put stress on joints, leading to conditions such as osteoarthritis. Maintaining a healthy BMI can alleviate pressure on joints and contribute to better joint health.
4. Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is often associated with obesity as a common risk factor. By maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can potentially reduce the severity of sleep apnea or prevent it altogether.
Balanced Diet and Physical Activity for a Healthy BMI
Achieving and maintaining a healthy BMI involves a balanced approach that includes proper nutrition and regular physical activity.
1. Nutrition Tips for a Healthy BMI
Focus on Whole Foods: Incorporate whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet.
Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating by being attentive to portion sizes, preventing overeating.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support overall health and prevent overeating due to thirst confusion.
Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: Minimize your intake of processed foods and sugary beverages, as they contribute to weight gain and offer little nutritional value.
2. Physical Activity Recommendations for BMI Management
Aerobic Exercises: Engage in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling to improve cardiovascular health and burn calories.
Strength Training: Incorporate strength training exercises to build muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and support weight management.
Stay Active Throughout the Day: Besides structured workouts, aim to be active throughout the day by taking short walks, using stairs, or participating in household chores.
Flexibility and Balance Exercises: Incorporate flexibility and balance exercises like yoga or tai chi to improve overall body mobility and stability.
Set Realistic Goals: Set achievable fitness goals and track your progress to stay motivated on your journey to a healthy BMI.
Body Mass Index is also applicable to children and adolescents, but the interpretation differs based on age and sex. Pediatric BMI charts take into account growth and development factors. If you are concerned about your child’s weight, consult a pediatrician or a qualified healthcare professional.
BMI and Pregnancy
During pregnancy, BMI plays a crucial role in assessing a woman’s weight and overall health. However, traditional BMI measurements may not be accurate during pregnancy due to changes in body composition. Pregnant individuals should work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor weight gain and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Is BMI the Only Indicator of Health?
While BMI is a valuable tool for assessing weight status, it is essential to remember that it is not the only indicator of overall health. Other factors, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood sugar, and lifestyle habits, also play a significant role in determining health status.
Regular health check-ups and screenings are vital to gaining a comprehensive understanding of your overall well-being.
Conclusion
Body Mass Index is a valuable tool in assessing weight status and its impact on overall health. By understanding your BMI and its significance, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of weight-related health conditions. Remember that BMI is just one piece of the puzzle. Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and overall healthy lifestyle habits are essential for achieving optimal well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a healthy BMI for adults?
A healthy BMI range for adults is typically between 18.5 to 24.9. This range is associated with lower health risks and is considered an indicator of a healthy weight.
Can Body Mass Index accurately determine body fat percentage?
Body Mass Index is a useful tool to estimate body fat, but it is not a direct measurement. For a more accurate assessment of body composition, methods like dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) or underwater weighing may be used.
Can BMI be affected by muscle mass?
Yes, BMI can be influenced by muscle mass. Individuals with a higher muscle mass may have a higher BMI, even if their body fat percentage is low. This is why BMI should be interpreted alongside other indicators of health.
Is BMI equally applicable to all ethnic groups?
Body Mass Index categories may not be equally applicable to all ethnic groups due to differences in body composition and fat distribution. Healthcare professionals take ethnicity into account when interpreting BMI results.
Should BMI be the sole factor in weight management?
No, BMI should not be the sole factor in weight management. It is essential to consider other factors, such as individual health goals, lifestyle habits, and medical history, when developing a weight management plan.
Can a person with a normal BMI still be unhealthy?
Yes, it is possible for an individual with a normal BMI to have other health issues. A normal BMI does not guarantee overall health, as factors like diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in well-being.
Can a person with a normal Body Mass Index still be unhealthy?
Yes, it is possible for an individual with a normal Body Mass Index to have other health issues. A normal BMI does not guarantee overall health, as factors like diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices also play a crucial role in well-being.
Disclaimer
As with any health-related concerns, it is advisable to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support. Embrace a holistic approach to your health journey, and your body will thank you for it.
Disclaimer
Remember that building wealth and achieving financial freedom require discipline, patience, and a long-term mindset. Implementing these four habits consistently can significantly impact your financial journey positively. Always seek professional advice when making major financial decisions to ensure your actions align with your unique circumstances and goals.
One Response