10 Causes of Stress and Anxiety in Children

Introduction
In today’s fast-paced and increasingly demanding world, stress and anxiety in children have become pressing concerns. Identifying the causes behind these overwhelming emotions is crucial for promoting their mental well-being and overall development. By gaining a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to stress and anxiety in children, parents, educators, and mental health professionals can work together to create supportive environments that foster resilience and emotional stability. This topic delves into the multifaceted aspects of childhood stress and anxiety, shedding light on the various triggers that may impact a child’s mental health, and exploring effective strategies to mitigate their effects.
The 10 Causes of Stress and Anxiety in Children
Understanding the root causes of stress and anxiety in children is essential to address their emotional well-being effectively. Several factors contribute to stress and anxiety in children and cause distress to children, include:
1. Academic Pressure:
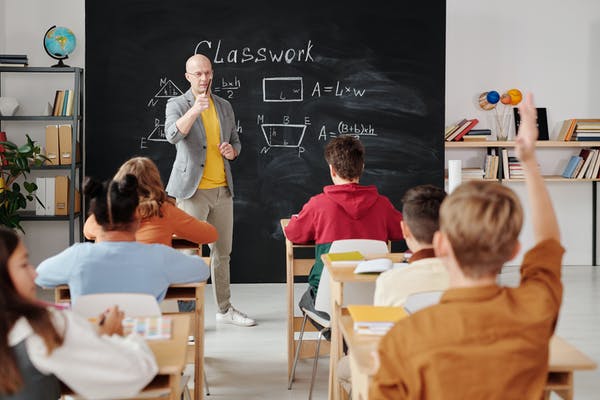

Academic pressure is another reason for stress and anxiety in children and can significantly impact school-age children, as the demands for academic excellence and performance expectations increase. In today’s competitive educational environment, children may face intense pressure to excel in their studies, achieve top grades, and meet the expectations set by parents, teachers, and society.
The pursuit of academic success can create a stressful environment, leaving children feeling overwhelmed and anxious. They may internalize the fear of failure, leading to self-doubt and a constant need to prove their worth through academic achievements.
The weight of academic pressure can manifest in various ways, such as sleep disturbances, loss of interest in learning, and a decline in self-esteem. Children may feel as if their value as individuals is solely determined by their academic performance, leading to an unhealthy focus on grades and comparisons with peers.
Caregivers and educators play a vital role in alleviating academic pressure and promoting a balanced approach to education. By fostering a supportive and nurturing environment, emphasizing the importance of effort over outcomes, and encouraging a love for learning, children can develop a positive attitude towards academics and overcome stress associated with academic pressure.
2. Family Changes:
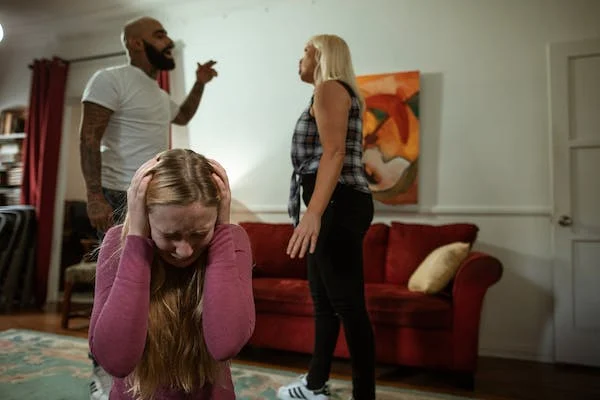
Family changes, such as divorce, relocation, or the arrival of a new sibling, can have a profound impact on children’s emotional well-being and trigger stress and anxiety in children. These significant life events disrupt familiar routines and may cause uncertainty and upheaval in the child’s life.
Divorce or separation can create feelings of instability and insecurity in children, as they may struggle to adjust to changes in living arrangements and family dynamics. Relocation to a new home or school can uproot a child from their support system and familiar surroundings, leading to feelings of isolation and anxiety.
The arrival of a new sibling can also evoke mixed emotions in children, ranging from excitement to jealousy and fear of reduced attention from caregivers. These emotions can be overwhelming for young children who are still learning to process their feelings.
During these family changes, it is crucial for caregivers to offer reassurance, communication, and emotional support. Creating an open and safe space for the child to express their feelings can help them cope with the anxiety and uncertainty associated with these transitions. Validating their emotions and providing age-appropriate explanations can promote a sense of security and understanding.

By acknowledging the potential impact of family changes on children’s emotional well-being and offering consistent support, caregivers can help children navigate through these transitions with resilience and emotional strength.
3. Peer Pressure:

Peer pressure can be a significant source of stress and anxiety in children, particularly during adolescence when social dynamics play a crucial role in shaping their identity and sense of belonging. As children strive to fit in and be accepted by their peers, they may encounter situations where they feel compelled to conform to group norms, even if it goes against their own values or beliefs.
The fear of rejection or being judged by peers can create immense pressure on children to engage in risky behaviors or make choices that may not align with their true selves. This internal conflict between the desire for social acceptance and staying true to their individuality can lead to heightened stress and anxiety.
Furthermore, the increasing influence of social media and online interactions intensifies the impact of peer pressure, as children may feel constant pressure to portray a certain image or keep up with unrealistic standards set by their peers.
Caregivers and educators play a critical role in supporting children through the challenges of peer pressure. Encouraging open communication and fostering a sense of self-esteem and self-worth can empower children to make independent decisions and resist negative peer influences. Teaching them assertiveness and conflict resolution skills can help them navigate social situations with confidence.
By acknowledging the impact of peer pressure on children’s emotional well-being and providing guidance and support, caregivers can help children develop resilience and coping strategies to navigate through peer interactions positively. Building a strong foundation of self-awareness and self-confidence can empower children to forge authentic connections with peers while staying true to their values and beliefs.
4. Traumatic Events:

Experiencing or witnessing traumatic events can profoundly affect a child’s emotional well-being and may develop stress and anxiety in children. Trauma can take various forms, such as accidents, natural disasters, violence, or the loss of a loved one. These distressing experiences can leave lasting emotional scars on children, impacting their mental health and behavior.
Traumatic events can lead to a range of emotional responses, including fear, anxiety, sadness, anger, and a sense of helplessness. Children may struggle to process these overwhelming emotions, and they may exhibit changes in behavior, such as withdrawal, irritability, or difficulty sleeping.
Caregivers and educators must recognize the signs of trauma in children and offer sensitive and supportive responses. Providing a safe environment for the child to express their feelings and fears is crucial. Professional support from mental health counselors can be instrumental in helping the child process the trauma and develop healthy coping mechanisms.
By acknowledging the impact of traumatic events on children and offering appropriate support and intervention, caregivers can play a vital role in helping children heal emotionally and regain a sense of safety and security. Creating a nurturing and understanding environment can facilitate the child’s journey towards recovery and emotional well-being.
5. Parental Expectations:
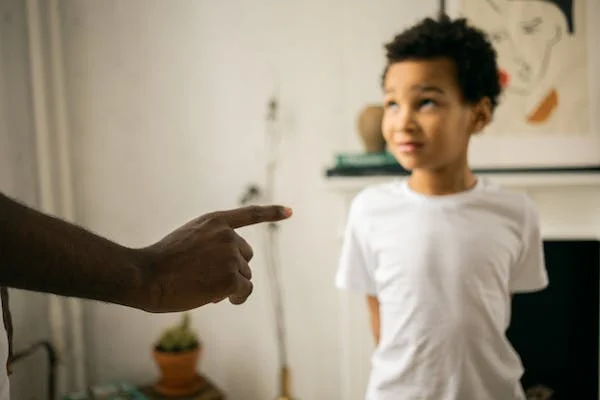

Overwhelming parental expectations and constant criticism can be significant sources of stress and anxiety in children. Parents often have high hopes and aspirations for their children’s success and well-being, which can inadvertently place immense pressure on them to meet these expectations.
Children may feel burdened by the need to constantly perform at a high level in academics, sports, or other areas to gain parental approval or avoid disappointment. This relentless pursuit of perfection can lead to feelings of inadequacy and stress, as children fear they may not live up to their parents’ standards.
Moreover, frequent criticism or negative feedback can erode a child’s self-esteem and confidence. The constant feeling of not being good enough or valued for who they are can be emotionally distressing for children.
It is crucial for parents to balance their expectations with understanding and support. Encouraging children’s efforts, regardless of outcomes, and fostering a nurturing environment can promote a positive self-image and reduce stress.
Open communication and active listening are vital in understanding children’s feelings and concerns. Creating an atmosphere where children feel comfortable expressing themselves without fear of judgment can help strengthen the parent-child bond and provide emotional security.
By being aware of the impact of parental expectations and criticism, parents can play a pivotal role in supporting their children’s emotional well-being. Celebrating their individual strengths and guiding them with compassion can contribute to a healthier parent-child relationship and promote a sense of emotional balance in children’s lives.
6. Media Influence:

Media influence, especially exposure to distressing news or violent media content, can have a profound impact on sensitive children and contribute to heightened stress and anxiety in children. In today’s digital age, children are constantly exposed to various forms of media, including television, social media, and online news platforms.
Distressing news stories, such as natural disasters, acts of violence, or global crises, can be overwhelming for children, causing them to feel anxious and fearful about their safety and the world around them. Additionally, violent media content, whether in movies, video games, or online videos, can evoke strong emotional responses in children and desensitize them to violence.
Sensitive children, in particular, may find it challenging to process and cope with the intense emotions evoked by media content. They may have difficulty differentiating between fiction and reality, leading to heightened anxiety and feelings of vulnerability.
Caregivers play a critical role in mitigating the impact of media influence on children. Limiting exposure to distressing or violent content, and providing age-appropriate explanations about media events can help children develop a healthy perspective and coping mechanisms. Encouraging open communication and creating a safe space for children to express their feelings and fears is essential in guiding them through the complexities of media influence.
By being mindful of media consumption and offering appropriate guidance and support, caregivers can protect sensitive children from unnecessary anxiety and foster their emotional well-being. Striking a balance between media exposure and emotional resilience can empower children to navigate the digital world with confidence and emotional intelligence.
7. Bullying and Cyberbullying:
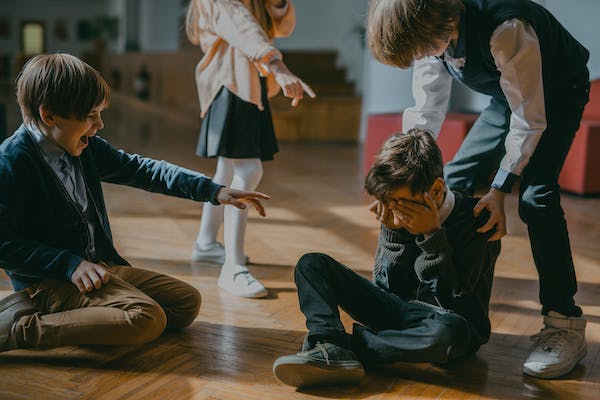

Being a victim of bullying, whether in-person or online (cyberbullying), can have severe and lasting effects on a child’s mental health and may cause stress and anxiety in children. Bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior, such as physical or verbal attacks, exclusion, or the spreading of rumors, with the intent to harm, intimidate, or control the victim.
Bullying can subject children to a myriad of emotional and psychological consequences when they become its victims. They may develop feelings of fear, anxiety, and low self-esteem, as the constant harassment undermines their sense of safety and self-worth. The emotional toll can lead to academic difficulties, social withdrawal, and even physical health issues.
Cyberbullying, with its pervasive and relentless nature, poses additional challenges to victims. Online platforms provide anonymity to bullies, making it easier to target and humiliate their victims from a distance. In the realm of cyberbullying, its digital essence ensnares victims, perpetuating harassment that relentlessly shadows them across numerous online platforms.
Being vigilant in recognizing signs of bullying and offering support to victims is crucial for caregivers, educators, and peers. Creating a culture of empathy and kindness can help prevent bullying and foster a safe and inclusive environment for all children. Encouraging open communication and offering resources for victims can empower them to seek help and report incidents of bullying.
Addressing bullying promptly and effectively is crucial in protecting the mental health and well-being of children. By taking a stand against bullying and promoting a culture of respect and compassion, we can create a safer and more supportive community where all children can thrive.
8. Health Issues:
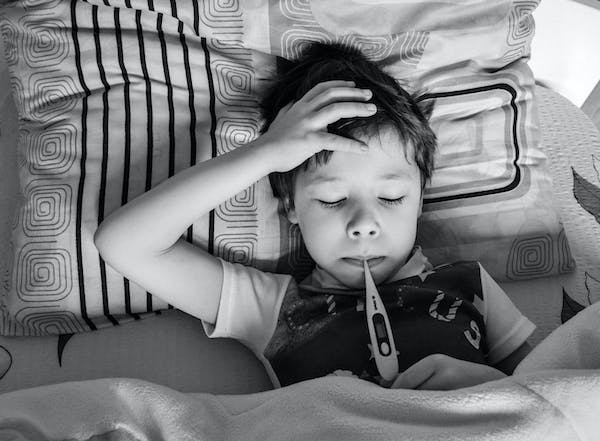

Health issues, whether chronic illnesses or medical procedures, can significantly impact a child’s emotional well-being and trigger stress and anxiety in children. Dealing with health challenges at a young age can be overwhelming, as it disrupts their sense of normalcy and exposes them to unfamiliar and often frightening experiences.
Children with chronic illnesses may grapple with ongoing medical treatments, frequent hospital visits, and limitations in their daily activities. The uncertainty surrounding their health condition can lead to feelings of vulnerability and anxiety about the future.
Medical procedures, even routine ones, can be distressing for children, causing fear and anxiety about pain, needles, or being separated from their caregivers. The unfamiliar hospital environment and interactions with medical professionals can also add to their stress.
Caregivers and healthcare providers play a crucial role in supporting children through health challenges. Providing age-appropriate explanations, being honest about medical procedures, and offering emotional support can help ease their anxiety and foster a sense of trust.
Creating a comforting and empathetic environment can empower children to cope with their health issues and build resilience. Encouraging them to express their feelings and concerns openly can help them process their emotions and develop a positive attitude towards their health journey.
By addressing the emotional aspect of health issues, we can help children navigate through the challenges with greater strength and emotional well-being. Supporting them with compassion and understanding can make a significant difference in their ability to cope and heal both physically and emotionally.
9. Family Finances:
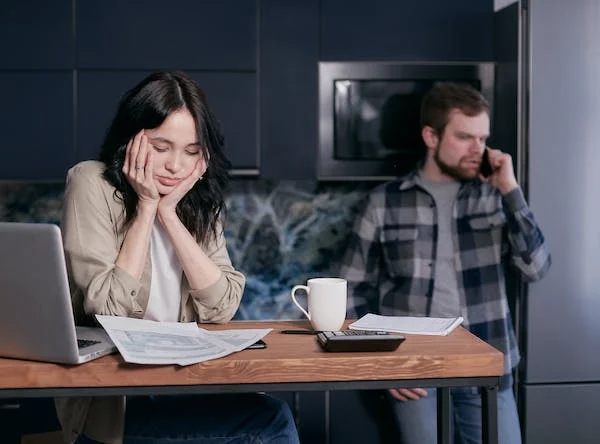

Family finances, particularly when facing financial difficulties, can significantly impact children and create an atmosphere of stress within the household. Economic challenges can lead to heightened tension and uncertainty, affecting the emotional well-being of children.
Children are sensitive to changes in their family’s financial situation, even if they may not fully comprehend the complexities of the issue. They may sense the stress and anxiety of their caregivers and absorb the emotional strain within the household.
Financial hardships can result in changes to the child’s daily life, such as limited access to resources, extracurricular activities, or even basic needs like nutritious meals and adequate housing. These changes can be distressing for children, leading to feelings of insecurity and vulnerability.
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to create an open and honest dialogue with children about family finances. Age-appropriate explanations can help children understand the situation without burdening them with unnecessary worries.
Offering emotional support and reassurance during difficult times is essential. Demonstrating resilience and positive coping strategies can also serve as a valuable example for children in learning to navigate through challenging circumstances.
Seeking external support, such as financial counseling or assistance programs, can help alleviate the immediate stress on the family and provide a more stable environment for the children.
By addressing the impact of financial difficulties on children and providing a supportive and understanding environment, parents can help children build emotional resilience and adapt to changing circumstances. Emphasizing the importance of love, communication, and togetherness can strengthen the family bond and foster emotional well-being, even in the face of financial challenges.
10. Overstimulation:

Overstimulation can overwhelm children, particularly when their schedules are packed with excessive extracurricular activities and limited downtime. In today’s fast-paced world, children often find themselves constantly engaged in various activities, leaving little time for relaxation and self-reflection.
The pressure to excel in academics, sports, and other pursuits can lead to a hectic lifestyle, leaving children with little opportunity to recharge and decompress. The constant stimulation from screens, technology, and social interactions can also contribute to overstimulation and ultimately may lead to stress and anxiety in children.
Children may experience heightened stress, anxiety, and fatigue as a result of overstimulation. They may struggle to focus, have difficulty falling asleep, or exhibit emotional outbursts due to the lack of sufficient downtime to process their thoughts and emotions.
As caregivers and educators, it is crucial to recognize the signs of overstimulation and prioritize the importance of balance and rest. Creating a structured schedule that allows for adequate downtime and self-directed play can promote a healthier and more balanced lifestyle.
Encouraging mindfulness practices, such as meditation or spending time in nature, can help children relax and reduce stress. Limiting screen time and ensuring that extracurricular activities are age-appropriate and enjoyable can also contribute to a more balanced and fulfilling childhood.
One Response